Toyota Diagnostic Fault Codes
TOYOTA error codes and statuses
2. DTC check (using sst check wire)
3. DTC check (using hand-held tester)
4. Input signal check (test mode)
5. Diagnostic codes
2. Outline of EPS system
3. Function of main components
4. Construction
5. Operation
6. Questions
Abreviaturas ecu Toyota
Abbreviations and Toyota/SAE terms:Glossary of SAE and Toyota Terms Download
Toyota Diagnostic Trouble Codes Full List-ObdII365 Download
Toyota - Diagnostic Trouble Codes Download
HIGHLANDER
3 generations, 2007
HILUX
4 generations, 2005
IQ
1st generation, 2009
LAND CRUISER
4 generations, 2007
LAND CRUISER PRADO
5 generations, 1996
PRIUS
5 generations, 2009
RAV4
7 generations, 2000
SIENNA
1st generation, 2018
SIENTA
1st generation, 2015
SUPRA
1st generation, 2020
URBAN CRUISER
1st generation, 2006
VENZA
2 generations, 2012
VERSO
2 generations, 2009
VERSO-S
1st generation, 2015
VIOS
1st generation, 2013
VOXY
1st generation, 2013
YARIS
2 generations, 2010
YARIS CROSS
1st generation, 2021
4RUNNER
1st generation, 2013
ALPHARD
3 generations, 2008
AURIS
3 generations, 2006
AVALON
3 generations, 2006
AVENSIS
5 generations, 1997
CAMRY
6 generations, 2001
CELICA
1st generation, 1999
C-HR
2 generations, 2017
COROLLA
6 generations, 2002
COROLLA CROSS
1st generation, 2021
CROWN
1st generation, 2012
FJ CRUISER
1st generation, 2010
FORTUNER
1st generation, 2016
GR 86
1st generation, 2022
GT 86
1st generation, 2011
HARRIER
1st generation, 2013
HIACE
2 generations, 2004
TOYOTA OBD TROUBLE CODES Download
What are U trouble codes?
What is DTC in Toyota?
How do I read a diagnostic trouble code?
How do I read my Toyota diagnostic code?
Technical defects appear sooner or later in cars of all manufacturers, including Japanese ones. The driver is able to decode Toyota error codes on his own, and it is possible to determine the malfunction of the systems without the use of scanners. If a car enthusiast has never encountered such a problem before, then this article will help to understand all the nuances and perform work at a professional level.
Diagnostics of Toyota cars
Diagnostics is available on vehicles of the entire Toyota model range and is divided into two types:
- mechanical;
- computer.
Before starting electronic diagnostics, the driver must make sure that all systems and basic mechanisms of the Toyota vehicle are in working order. To do this, you should check the fuses, wiring, and also examine the connections and vehicle components for breakages.
If any serious problem is found, then it must be eliminated, and only then carry out computer diagnostics, which happens:
- preliminary;
- post-accident;
- planned;
- pre-sale.
How do you read diagnostic trouble codes?
What is a vehicle diagnostic trouble code?
How many diagnostic trouble codes are there?
What does a diagnostic trouble code DTC indicate?
Step-by-step self-diagnosis
For self-diagnostics, the driver needs to work with DLC 1 and DLC 2. This abbreviation stands for Data Link Connector. DLC 1 looks like a plastic box with a lid on top. Located under the hood, most often on the left. It is easy to find by the Diagnostic label.

In older models, the diagnostic connector is made in the form of a yellow circle and is located near the battery. There are no DLC2 details in cars like the Corolla AE 100.
Fault codes of older car models: Toyota Corona 1992, Karina 1992-97, Toyota Mark are read only by flashing indicators.
In the new models, DLC 2 is located directly in the cabin, under the dashboard and at the feet near the steering wheel. Most often it is round and is used during the inspection carried out with the help of special equipment.

During self-diagnosis by closing individual contacts of the connector, only by connecting them in the desired sequence, you can get the correct code for decryption.
To find out about the presence of faults in the engine and / or gearbox system, the following steps will help:
- Find the first DLC 1 connector labeled Diagnostic.
- Remove or unscrew the protective cover of the box. Below it there should be a diagram indicating the outputs of the connector.
- Take a wire, piece of wire, or other thin metal object (such as a paper clip) and place a jumper between the pins labeled TE1 and E1.
- Switch on the ignition. Check that the stove or air conditioner is not working.
- Look at the O / D lamps (for the gearbox) and the Check Engine (for the engine). Memorize or write down the number and intervals of blinking of the indicators.

Everything is in order with the car and no breakdowns with the internal combustion engine and transmission were found if:
- indicators flashed evenly with the same interval and duration of light more than 11 times;
- The Check Engine light is illuminated for a long time and evenly at intervals of 4.5 s (this means that the code is given using type 10).
Any other combinations of light bulbs indicate malfunctions in the operation of engine systems, gearboxes or other mechanisms in the car.
If the circuit on the back of the cover is erased, you cannot find the contact or are not sure that you have closed the right one, you must:
- Switch on the ignition.
- Connect one of the test lamp wires to ground (to the car body).
- Connect the second wire to each pin of the connector in turn.
- Complete the check when the Check Engine light on the panel starts flashing.
It will be more convenient if someone helps to follow the light bulb while you change the position of the wire.
Recognize fault codes using two systems of flashing lights.
The first setting option will allow you to find out the errors indicated by a two-digit code (type 09):
- showing the code, the light comes on for a split second;
- the time interval between pulses is also a fraction of a second;
- pause between tens and ones in one code 1.5 s;
- break between different codes 2 and a half seconds;
- series of combinations of different faults are separated by 4.5 s.
The 10th setting type defines unambiguous codes. Here the light "flashes" the exact number of the error.
Such code should be "read" according to the following rules:
- the duration of the indicator glow within one impulse - 0.5 s;
- the pause between flashes within the same code lasts half a second;
- break between different codes - 2.5 s;
- a series of combinations of breakdowns are separated by a pause of 4.5 s.
Breakdowns in the ABS system are determined according to the same scheme, but the terminals TC and E1 are closed. DTCs SRS and 4WS are calculated by the corresponding sensor with the same closed contacts as in ABS.
Decoding of faults
Type 9 error codes common to all Toyota vehicles are represented by two-digit codes.
Code / Decoding
11 No power to EFI unit
12 No signal from the engine speed sensor
13 No signal from the engine speed sensor at speeds over 1000 rpm
14 There is no signal from the "minus" of the ignition coil or from the "minus" of the coil number one (if there are two of them)
15 There is no signal from the "minus" of the ignition coil number two
16 No communication between the automatic transmission control unit and the engine control unit
17 Incorrect signal from the camshaft position sensor number 1
18 Incorrect signal from the camshaft position sensor number 2
21 Incorrect signal from the oxygen sensor, if the engine is V-shaped, then the heater of the left main oxygen sensor is faulty
22 Incorrect signal from the engine temperature sensor (THW)
23 Incorrect signal from the intake air temperature sensor (THA)
24 Incorrect signal from the intake air temperature sensor (THA)
25 Too lean mixture
26 Too rich mixture
27 Incorrect signal from the additional oxygen sensor (left in V-shaped engines)
28 Incorrect signal from the oxygen sensor (for V-shaped engines, the heater of the right main oxygen sensor)
29 The additional oxygen sensor is faulty (right in V-shaped engines)
31 Incorrect signal from the air flow sensor or, if not, from the pressure sensor in the intake manifold (vacuum sensor)
32 Incorrect signal from the air flow sensor
34 Defective boost
35 Wrong signal from the atmospheric pressure sensor in the intake manifold (vacuum sensor)
38 Automatic transmission fluid temperature sensor
41 Wrong signal from the throttle position sensor (TPS)
42 Incorrect signal from the vehicle speed sensor (speedometer)
43 No starter signal (STA) to the engine control unit
46 Defective solenoid valve number 4 or its circuit
47 Defective additional throttle position sensor (TPS) or its circuit
48 Defective auxiliary air supply control system
51 No idle signal from TPS
52 Wrong signal from the knock sensor (if there are two of them, then from the left or from the front)
53 Problems in the knock sensor control circuits (ignition timing)
55 Wrong signal from the knock sensor (if there are two of them, then from the right or from the rear)
61 The main speed sensor or its circuit is faulty
62 Defective solenoid valve number 1 or its circuit
63 Defective solenoid valve number 2 or its circuit
64 Defective solenoid valve number 3 or its circuit
65 Defective solenoid valve number 4 or its circuit
67 The sensor of inclusion of O / D or its circuit is faulty
71 Defective EGR control system
72 Solenoid fuel cut
77 Defective pressure control solenoid or its circuit (in the machine)
78 There is no signal to the fuel pump or its circuits are faulty
81 Faulty circuit between TCM and ECT1
82 Defective circuit between TCM and ESA1
84 Defective circuit between TCM and ESA2
85 Faulty circuit between TCM and ESA3
86 Faulty engine speed sensor
88 The circuit from the engine control unit to the automatic transmission control unit is faulty
89 Lost Communication Between Engine Control Unit and TRC Control Unit
99 No trouble codes
The general list of unambiguous codes (type-10) for a Toyota car consists of the following items.
Code Decoding
1 No breakdowns
2 The air flow sensor is giving a signal incorrectly
3 Incorrect signal from the communicator
4 The coolant temperature is out of range, the sensor is out of order
5 Incorrect communication with the oxygen sensor
6 The breakdown lies in the engine speed
7 Throttle valve in the wrong position
8 Sensor shows incorrect intake air temperature
9 Problem with vehicle speed
10 No starter enable signal
11 Broken air conditioner or faulty toggle switch responsible for the neutral position in the car
Gasoline internal combustion engines
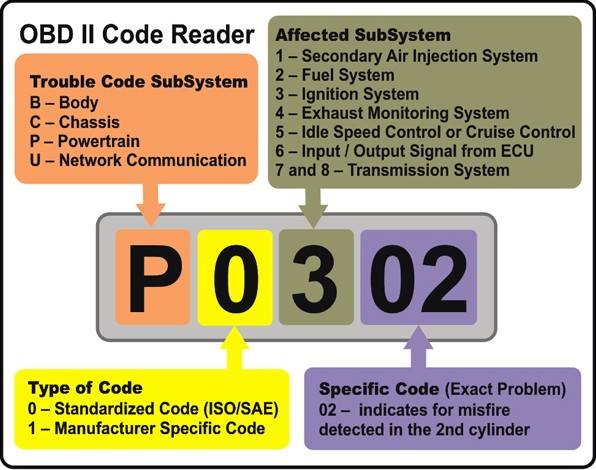
If the car has an on-board computer or a robot, then the code will appear on the mileage screen. It will consist of a Latin letter at the beginning, for example P, B, C, and 4 digits. This is typical for such cars as Toyota Rav 4 Avensis, Corolla, Mark II or Land Cruiser 200, Toyota Prado 120 and others that run on gasoline.
Table for decoding diagnostic trouble codes for gasoline internal combustion engines.
|
Codes |
Decoding |
Analogue on BC |
|
12 and 13 |
Crankshaft Position Sensor Problems |
P0335, P0335, P1335 |
|
14 and 15 |
Problems in the ignition system or with the coils |
P1300 and P1315, P1305 and P1310 |
|
18 |
System VVT- i phase |
P1346 |
|
nineteen |
The position of the pedal accelerator |
P1120 and P1121 |
|
21 |
Oxygen sensor |
P0135 |
|
22 |
The temperature of the cooling liquid |
P0115 |
|
24 |
Intake air temperature sensor breakage |
P0110 |
|
25 |
Oxygen sensor - lean mixture |
P0171 |
|
31 |
Absolute pressure sensor |
P0105 and P0106 |
|
36 |
CPS sensor |
P1105 |
|
39 |
VVT- i system |
P1656 |
|
41 |
The position of the throttle valve |
P0120, P0121 |
|
42 |
Vehicle speed sensor problems |
P0500 |
|
49 |
Fuel pressure D-4 |
P0190, P0191 |
|
52 and 55 |
Knock sensor breakage |
P0325 |
|
58 |
SCV drive |
P1415, P1416, P1653 |
|
59 |
Wrong VVT- i signal |
P1349 |
|
71 |
EGR system |
P0401, P0403 |
|
89 |
ETCS drive |
P1125, P1126, P1127, P1128, P1129, P1633 |
|
92 |
Cold start nozzle problems |
P1210 |
|
97 |
Injector defective |
P1215 |
Diesel Engines
Many Toyota cars were produced with a diesel engine. The most popular models are Vitz sedans, Caldina, Avensis (T25), Camry, Camry Gracia, Corolla E150, Auris 2008, Land Cruiser Prado 120 and Land Cruiser Prado 200 SUVs or RAV4 crossover.
When writing down codes for diesel cars, you can see the following designations.
Code Decoding
13 Speed out of permissible limits
19 Incorrect position of the accelerator pedal
22 Malfunction in coolant temperature readings
24 Incorrect intake air temperature data
35 Charge pressure out of range
39 Fuel temperature sensors work poorly
42 The fault lies in the vehicle speed sensor
96 Position of the EGR valve is incorrect
Breakdown of other parts of the diesel engine.
Code Decoding
12 Problem in crankshaft position
14 Breakage in the valve that regulates the injection timing
15 Throttle servo is out of order
17 Incorrect signal coming from the control unit
18 Breakage in the solenoid bypass valve
32 Broken correction resistors
Automatic transmission
Cars of the same brand differ not only in the engine, but also in the gearbox. For the same Toyota Corolla 150, Celsior or Vista, automatic transmission breakdowns will differ from the “mechanics” malfunctions.
If the transmission is malfunctioning, you will see one of the codes.
|
Code |
Decoding |
Analogue for automatic gearbox |
|
37 |
Malfunction of the gearbox input speed sensor |
P1705 |
|
42, 44, 36 |
The problem is in the speed sensor (maybe the shaft speed) |
P0500 |
|
46 |
Pressure accumulator , faulty solenoid |
P1765 |
|
62, 63 |
Problems with one of the solenoids |
P0753 P0758 |
|
64, 68 |
Torque converter lockup clutch, solenoid defective |
P0773
|
Such errors are typical for different models, including Toyota Ipsum, Toyota Highlander 2001 and Caldina.
Other combinations
For diagnostics, special equipment and devices are also used. Such devices will display five-digit codes. They can also be recognized using the on-board computer, which is installed in new cars and hybrid models.
Code on the screen Toyota with on-board computer
The hybrid version includes Toyota Estima, Toyota Prius, third generation Toyota Harrier and others. These models (in addition to other breakdowns) may experience malfunctions of the high-voltage battery system (HVB). The hybrid installation error codes and their meanings are shown in the table.

Code Decoding
P1604 Engine start failed, breakdown in the intake system
B0101 The security system does not work correctly, problems with the protective cushions
In 1801, the chains of the squib are cut off from the driver's side
C1201 The engine is not working correctly, the speed is below the permissible
P0420 Catalyst system B1 is operating below the permissible efficiency threshold
P0352З Malfunctions in the ignition system circuits
Reset errors
After the repair was made and the breakdown was eliminated, the error codes may not disappear by themselves. To reset them, there is also a certain sequence of actions. To do this, we again need a diagnostic connector.
To reset the codes, you must:
Switch on the ignition.
On the DLC1 connector, close the TC and E1 terminals with a piece of wire or wires.
In 3 seconds, press the brake as many times as possible, but not less than 8 times.
Make sure the light blinks evenly at half-second intervals.
Switch off the ignition and remove the jumper from the contacts.
Make sure the ABS indicator is off.




